

Next: Pitfalls of Markov chain
Up: Priors and proposals
Previous: Proposals for the parameters
Contents
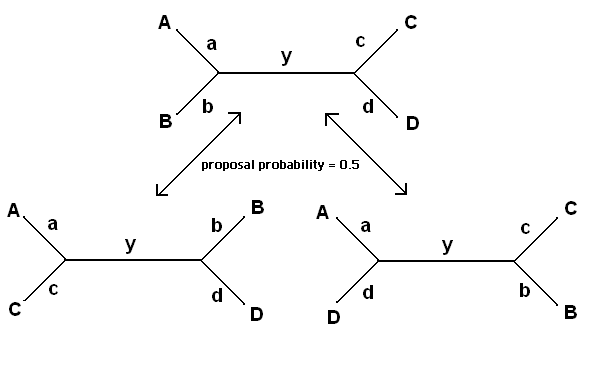
The tree topology is perturbed every ten cycles with either the nearest
neighbor interchange (NNI) proposal shown in figure 2.7
or the subtree pruning and re-grafting (SPR) proposal (Swofford et al., 1996)
shown in figure 2.8.
Each cycle a randomly chosen branch length is modified with a figure
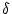 drawn from a normal distribution centred at zero.
When the branch length becomes negative special rules which can lead
to a topology change are applied (Jow et al., 2002). If the branch
is an internal branch then one of the two nearest neighbor topologies is
proposed with each having equal probability; this is the Nearest Neighbour
Interchange described above. The new internal branch
length is set to
drawn from a normal distribution centred at zero.
When the branch length becomes negative special rules which can lead
to a topology change are applied (Jow et al., 2002). If the branch
is an internal branch then one of the two nearest neighbor topologies is
proposed with each having equal probability; this is the Nearest Neighbour
Interchange described above. The new internal branch
length is set to
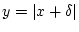 (see figure
2.9). If the branch is a terminal branch, we cannot
apply the NNI algorithm and we simply use a reflecting boundary.
The new proposed length is
(see figure
2.9). If the branch is a terminal branch, we cannot
apply the NNI algorithm and we simply use a reflecting boundary.
The new proposed length is
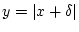 .
The acceptance rate for the SPR and the NNI proposals are usually
quite low. The ``local'' NNI proposal, induced by a branch length
modification, has a better acceptance rate.
.
The acceptance rate for the SPR and the NNI proposals are usually
quite low. The ``local'' NNI proposal, induced by a branch length
modification, has a better acceptance rate.



Next: Pitfalls of Markov chain
Up: Priors and proposals
Previous: Proposals for the parameters
Contents
Gowri-Shankar Vivek
2003-04-24